밑이 자연상수 e인 지수함수
x = np.arange(-2, 4, 0.1)
y = np.exp(x)
plt.plot(x, y, label='e^x')
plt.legend()
plt.show()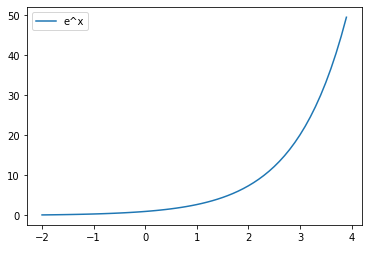
자연로그 함수
x = np.arange(0.1, 4, 0.1)
y = np.log(x)
plt.plot(x, y, label='y = log x')
plt.legend()
plt.show()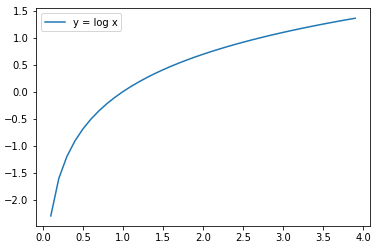
지수 함수 curve fitting
from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# a*e^(-b*x)+c
def func1(x, a, b, c):
return a * np.exp(-b * x) + c
def func2(x, a, b, c):
return a * pow(2.7182, -b * x) + c
def custom_curve_fit(xdata, ydata):
popt1, pcov1 = curve_fit(func1, xdata, ydata)
# r^2 계산
residuals1 = ydata - func1(xdata, *popt1)
ss_res1 = np.sum(residuals1**2)
ss_tot = np.sum((ydata-np.mean(ydata))**2)
r1 = 1 - (ss_res1 / ss_tot)
return popt1, r1
xdata = np.linspace(0, 4, 50)
y = func1(xdata, 2.5, 1.3, 0.5)
np.random.seed(1729)
y_noise = 0.2 * np.random.normal(size=xdata.size)
ydata = y + y_noise
plt.plot(xdata, ydata, 'b-', label='data')
p1, r1 = custom_curve_fit(xdata, ydata)
print(f'R^2 : {r1}')
plt.plot(xdata, func1(xdata, *p1), 'r-', label='fit: a=%5.3f, b=%5.3f, c=%5.3f' % tuple(p1))
plt.plot(xdata, func2(xdata, 2.5, 1.3, 0.5), 'g-', label='2.5*2.7182^(-b*x)+0.5')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
2차 다항식
from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ax^2+bx+c
def func(x, a, b, c):
return a*pow(x,2)+b*x+c
xdata = np.arange(1000, 11000, 1000)
ydata = [1, 1.7, 2.4, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.4, 4.9, 5.3, 5.7]
plt.plot(xdata, ydata, '*-')
popt, pcov = curve_fit(func, xdata, ydata)
plt.plot(xdata, func(xdata, *popt), 'r-', label='fit: a=%5.3f, b=%5.3f, c=%5.3f' % tuple(popt))
plt.legend()
plt.show()
popt
Least squares - 최소제곱법
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EC%B5%9C%EC%86%8C%EC%A0%9C%EA%B3%B1%EB%B2%95
최소제곱법 - 위키백과, 우리 모두의 백과사전
위키백과, 우리 모두의 백과사전. 붉은 점들을 기반으로 푸른 선의 2차 방정식 근사해를 구한다. 최소제곱법, 또는 최소자승법, 최소제곱근사법, 최소자승근사법(method of least squares, least squares app
ko.wikipedia.org
비선형 최소제곱법
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-linear_least_squares
Non-linear least squares - Wikipedia
Non-linear least squares is the form of least squares analysis used to fit a set of m observations with a model that is non-linear in n unknown parameters (m ≥ n). It is used in some forms of nonlinear regression. The basis of the method is to approxim
en.wikipedia.org
https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.curve_fit.html
scipy.optimize.curve_fit — SciPy v1.5.2 Reference Guide
Function with signature jac(x, ...) which computes the Jacobian matrix of the model function with respect to parameters as a dense array_like structure. It will be scaled according to provided sigma. If None (default), the Jacobian will be estimated numeri
docs.scipy.org
https://github.com/scipy/scipy/blob/v1.5.2/scipy/optimize/minpack.py#L532-L834
scipy/scipy
Scipy library main repository. Contribute to scipy/scipy development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
Non-linear 최소제곱법
def curve_fit(f, xdata, ydata, p0=None, sigma=None, absolute_sigma=False,
check_finite=True, bounds=(-np.inf, np.inf), method=None,
jac=None, **kwargs):
"""
Use non-linear least squares to fit a function, f, to data.
Assumes ``ydata = f(xdata, *params) + eps``.
Parameters
----------
f : callable
The model function, f(x, ...). It must take the independent
variable as the first argument and the parameters to fit as
separate remaining arguments.
xdata : array_like or object
The independent variable where the data is measured.
Should usually be an M-length sequence or an (k,M)-shaped array for
functions with k predictors, but can actually be any object.
ydata : array_like
The dependent data, a length M array - nominally ``f(xdata, ...)``.
p0 : array_like, optional
Initial guess for the parameters (length N). If None, then the
initial values will all be 1 (if the number of parameters for the
function can be determined using introspection, otherwise a
ValueError is raised).
sigma : None or M-length sequence or MxM array, optional
Determines the uncertainty in `ydata`. If we define residuals as
``r = ydata - f(xdata, *popt)``, then the interpretation of `sigma`
depends on its number of dimensions:
- A 1-D `sigma` should contain values of standard deviations of
errors in `ydata`. In this case, the optimized function is
``chisq = sum((r / sigma) ** 2)``.
- A 2-D `sigma` should contain the covariance matrix of
errors in `ydata`. In this case, the optimized function is
``chisq = r.T @ inv(sigma) @ r``.
.. versionadded:: 0.19
None (default) is equivalent of 1-D `sigma` filled with ones.
absolute_sigma : bool, optional
If True, `sigma` is used in an absolute sense and the estimated parameter
covariance `pcov` reflects these absolute values.
If False (default), only the relative magnitudes of the `sigma` values matter.
The returned parameter covariance matrix `pcov` is based on scaling
`sigma` by a constant factor. This constant is set by demanding that the
reduced `chisq` for the optimal parameters `popt` when using the
*scaled* `sigma` equals unity. In other words, `sigma` is scaled to
match the sample variance of the residuals after the fit. Default is False.
Mathematically,
``pcov(absolute_sigma=False) = pcov(absolute_sigma=True) * chisq(popt)/(M-N)``
check_finite : bool, optional
If True, check that the input arrays do not contain nans of infs,
and raise a ValueError if they do. Setting this parameter to
False may silently produce nonsensical results if the input arrays
do contain nans. Default is True.
bounds : 2-tuple of array_like, optional
Lower and upper bounds on parameters. Defaults to no bounds.
Each element of the tuple must be either an array with the length equal
to the number of parameters, or a scalar (in which case the bound is
taken to be the same for all parameters). Use ``np.inf`` with an
appropriate sign to disable bounds on all or some parameters.
.. versionadded:: 0.17
method : {'lm', 'trf', 'dogbox'}, optional
Method to use for optimization. See `least_squares` for more details.
Default is 'lm' for unconstrained problems and 'trf' if `bounds` are
provided. The method 'lm' won't work when the number of observations
is less than the number of variables, use 'trf' or 'dogbox' in this
case.
.. versionadded:: 0.17
jac : callable, string or None, optional
Function with signature ``jac(x, ...)`` which computes the Jacobian
matrix of the model function with respect to parameters as a dense
array_like structure. It will be scaled according to provided `sigma`.
If None (default), the Jacobian will be estimated numerically.
String keywords for 'trf' and 'dogbox' methods can be used to select
a finite difference scheme, see `least_squares`.
.. versionadded:: 0.18
kwargs
Keyword arguments passed to `leastsq` for ``method='lm'`` or
`least_squares` otherwise.
Returns
-------
popt : array
Optimal values for the parameters so that the sum of the squared
residuals of ``f(xdata, *popt) - ydata`` is minimized.
pcov : 2-D array
The estimated covariance of popt. The diagonals provide the variance
of the parameter estimate. To compute one standard deviation errors
on the parameters use ``perr = np.sqrt(np.diag(pcov))``.
How the `sigma` parameter affects the estimated covariance
depends on `absolute_sigma` argument, as described above.
If the Jacobian matrix at the solution doesn't have a full rank, then
'lm' method returns a matrix filled with ``np.inf``, on the other hand
'trf' and 'dogbox' methods use Moore-Penrose pseudoinverse to compute
the covariance matrix.
Raises
------
ValueError
if either `ydata` or `xdata` contain NaNs, or if incompatible options
are used.
RuntimeError
if the least-squares minimization fails.
OptimizeWarning
if covariance of the parameters can not be estimated.
See Also
--------
least_squares : Minimize the sum of squares of nonlinear functions.
scipy.stats.linregress : Calculate a linear least squares regression for
two sets of measurements.
Notes
-----
With ``method='lm'``, the algorithm uses the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm
through `leastsq`. Note that this algorithm can only deal with
unconstrained problems.
Box constraints can be handled by methods 'trf' and 'dogbox'. Refer to
the docstring of `least_squares` for more information.
Examples
--------
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
>>> def func(x, a, b, c):
... return a * np.exp(-b * x) + c
Define the data to be fit with some noise:
>>> xdata = np.linspace(0, 4, 50)
>>> y = func(xdata, 2.5, 1.3, 0.5)
>>> np.random.seed(1729)
>>> y_noise = 0.2 * np.random.normal(size=xdata.size)
>>> ydata = y + y_noise
>>> plt.plot(xdata, ydata, 'b-', label='data')
Fit for the parameters a, b, c of the function `func`:
>>> popt, pcov = curve_fit(func, xdata, ydata)
>>> popt
array([ 2.55423706, 1.35190947, 0.47450618])
>>> plt.plot(xdata, func(xdata, *popt), 'r-',
... label='fit: a=%5.3f, b=%5.3f, c=%5.3f' % tuple(popt))
Constrain the optimization to the region of ``0 <= a <= 3``,
``0 <= b <= 1`` and ``0 <= c <= 0.5``:
>>> popt, pcov = curve_fit(func, xdata, ydata, bounds=(0, [3., 1., 0.5]))
>>> popt
array([ 2.43708906, 1. , 0.35015434])
>>> plt.plot(xdata, func(xdata, *popt), 'g--',
... label='fit: a=%5.3f, b=%5.3f, c=%5.3f' % tuple(popt))
>>> plt.xlabel('x')
>>> plt.ylabel('y')
>>> plt.legend()
>>> plt.show()
"""
if p0 is None:
# determine number of parameters by inspecting the function
sig = _getfullargspec(f)
args = sig.args
if len(args) < 2:
raise ValueError("Unable to determine number of fit parameters.")
n = len(args) - 1
else:
p0 = np.atleast_1d(p0)
n = p0.size
lb, ub = prepare_bounds(bounds, n)
if p0 is None:
p0 = _initialize_feasible(lb, ub)
bounded_problem = np.any((lb > -np.inf) | (ub < np.inf))
if method is None:
if bounded_problem:
method = 'trf'
else:
method = 'lm'
if method == 'lm' and bounded_problem:
raise ValueError("Method 'lm' only works for unconstrained problems. "
"Use 'trf' or 'dogbox' instead.")
# optimization may produce garbage for float32 inputs, cast them to float64
# NaNs cannot be handled
if check_finite:
ydata = np.asarray_chkfinite(ydata, float)
else:
ydata = np.asarray(ydata, float)
if isinstance(xdata, (list, tuple, np.ndarray)):
# `xdata` is passed straight to the user-defined `f`, so allow
# non-array_like `xdata`.
if check_finite:
xdata = np.asarray_chkfinite(xdata, float)
else:
xdata = np.asarray(xdata, float)
if ydata.size == 0:
raise ValueError("`ydata` must not be empty!")
# Determine type of sigma
if sigma is not None:
sigma = np.asarray(sigma)
# if 1-D, sigma are errors, define transform = 1/sigma
if sigma.shape == (ydata.size, ):
transform = 1.0 / sigma
# if 2-D, sigma is the covariance matrix,
# define transform = L such that L L^T = C
elif sigma.shape == (ydata.size, ydata.size):
try:
# scipy.linalg.cholesky requires lower=True to return L L^T = A
transform = cholesky(sigma, lower=True)
except LinAlgError:
raise ValueError("`sigma` must be positive definite.")
else:
raise ValueError("`sigma` has incorrect shape.")
else:
transform = None
func = _wrap_func(f, xdata, ydata, transform)
if callable(jac):
jac = _wrap_jac(jac, xdata, transform)
elif jac is None and method != 'lm':
jac = '2-point'
if 'args' in kwargs:
# The specification for the model function `f` does not support
# additional arguments. Refer to the `curve_fit` docstring for
# acceptable call signatures of `f`.
raise ValueError("'args' is not a supported keyword argument.")
if method == 'lm':
# Remove full_output from kwargs, otherwise we're passing it in twice.
return_full = kwargs.pop('full_output', False)
res = leastsq(func, p0, Dfun=jac, full_output=1, **kwargs)
popt, pcov, infodict, errmsg, ier = res
ysize = len(infodict['fvec'])
cost = np.sum(infodict['fvec'] ** 2)
if ier not in [1, 2, 3, 4]:
raise RuntimeError("Optimal parameters not found: " + errmsg)
else:
# Rename maxfev (leastsq) to max_nfev (least_squares), if specified.
if 'max_nfev' not in kwargs:
kwargs['max_nfev'] = kwargs.pop('maxfev', None)
res = least_squares(func, p0, jac=jac, bounds=bounds, method=method,
**kwargs)
if not res.success:
raise RuntimeError("Optimal parameters not found: " + res.message)
ysize = len(res.fun)
cost = 2 * res.cost # res.cost is half sum of squares!
popt = res.x
# Do Moore-Penrose inverse discarding zero singular values.
_, s, VT = svd(res.jac, full_matrices=False)
threshold = np.finfo(float).eps * max(res.jac.shape) * s[0]
s = s[s > threshold]
VT = VT[:s.size]
pcov = np.dot(VT.T / s**2, VT)
return_full = False
warn_cov = False
if pcov is None:
# indeterminate covariance
pcov = zeros((len(popt), len(popt)), dtype=float)
pcov.fill(inf)
warn_cov = True
elif not absolute_sigma:
if ysize > p0.size:
s_sq = cost / (ysize - p0.size)
pcov = pcov * s_sq
else:
pcov.fill(inf)
warn_cov = True
if warn_cov:
warnings.warn('Covariance of the parameters could not be estimated',
category=OptimizeWarning)
if return_full:
return popt, pcov, infodict, errmsg, ier
else:
return popt, pcov
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
def custom_curve_fit(xdata, ydata):
'''
xdata = np.append(xdata, 0)
ydata = np.append(ydata, 0)
xdata = np.append(xdata, 5)
ydata = np.append(ydata, 8)'''
def func0(x, a, b):
return a*pow(b, x) #a * np.exp(b * x)
# a*x+b
# a*np.log(x)+b
def func1(x, a, b):
return a*pow(x,b)
def func2(x, a, b):
return a*pow(x,3)+b
def func3(x, a, b, c, d):
return a*pow(x,3)+b*pow(x,2)+c*x+d
def func4(x, a, b):
return a*pow(x,3)+b*pow(x,2)
popt0, pcov0 = curve_fit(func0, xdata, ydata, maxfev=2000)
popt1, pcov1 = curve_fit(func1, xdata, ydata, maxfev=2000)
popt2, pcov2 = curve_fit(func2, xdata, ydata, maxfev=2000)
popt3, pcov3 = curve_fit(func3, xdata, ydata, maxfev=2000)
popt4, pcov4 = curve_fit(func4, xdata, ydata, maxfev=2000)
residuals0 = ydata - func0(xdata, *popt0)
residuals1 = ydata - func1(xdata, *popt1)
residuals2 = ydata - func2(xdata, *popt2)
residuals3 = ydata - func3(xdata, *popt3)
residuals4 = ydata - func4(xdata, *popt4)
ss_res0 = np.sum(residuals0**2)
ss_res1 = np.sum(residuals1**2)
ss_res2 = np.sum(residuals2**2)
ss_res3 = np.sum(residuals3**2)
ss_res4 = np.sum(residuals4**2)
ss_tot = np.sum((ydata-np.mean(ydata))**2)
r0 = 1 - (ss_res0 / ss_tot)
r1 = 1 - (ss_res1 / ss_tot)
r2 = 1 - (ss_res2 / ss_tot)
r3 = 1 - (ss_res3 / ss_tot)
r4 = 1 - (ss_res4 / ss_tot)
return popt0, popt1, popt2, popt3, popt4, r0, r1, r2, r3, r4
file = 'input'
df = pd.read_excel(f'{file}.xlsx')
df2 = pd.DataFrame()
p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, r0, r1, r2, r3, r4 = custom_curve_fit(df['x'], df['y'])
df['y(ax^b)'] = p1[0]*pow(df['x'], p1[1])
df['y(dx3+cx2+bx+a)'] = p3[0]*pow(df['x'], 3) + p3[1]*pow(df['x'], 2) + p3[2]*df['x'] + p3[3]
df2 = df2.append({'a(ax^b)': p1[0],
'b(ax^b)': p1[1],
'r2(ax^b)': r1,
'a(dx3+cx2+bx+a)': p3[0],
'b(dx3+cx2+bx+a)': p3[1],
'c(dx3+cx2+bx+a)': p3[2],
'd(dx3+cx2+bx+a)': p3[3],
'r2(dx3+cx2+bx+a)': r3,
}, ignore_index=True)
writer = pd.ExcelWriter(f'{file}_RESULT.xlsx', engine='xlsxwriter')
df2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name = 'Sheet1')
df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name = 'Sheet2')
# Auto-adjust columns' width
for column in df2:
column_width = max(df2[column].astype(str).map(len).max(), len(column))
col_idx = df2.columns.get_loc(column)
print(col_idx, column, column_width)
writer.sheets['Sheet1'].set_column(col_idx, col_idx+1, column_width)
for column in df:
column_width = max(df[column].astype(str).map(len).max(), len(column))
col_idx = df.columns.get_loc(column)
writer.sheets['Sheet2'].set_column(col_idx, col_idx+1, column_width)
writer.save()
os.popen(f'./{file}_RESULT.xlsx')
'Python > Basic' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] Pillow 이미지 사이즈 확인 (0) | 2022.08.06 |
|---|---|
| [Python] PDF 관련 패키지 정리 (2) | 2022.08.05 |
| [Python] 파일 관련 (0) | 2022.07.19 |
| [Python] Excel, Word 다루기 (0) | 2021.07.26 |
| [Python] XlsxWriter - Excel 다루기 (0) | 2021.07.26 |